Simplifying Microservices Architecture for the Edge and AI Era
Watch Jean-Noel present on this topic at DBTA’s Microservices Architectures in the Era of Edge and AI webinar
Microservices have transformed how we build and scale applications, but as systems extend to the edge and integrate with AI-driven workloads, complexity skyrockets.
Traditional architectures depend on several components—such as service discovery, load balancers, API gateways, and message brokers—to manage communication between services. This reliance creates a tangled web of dependencies that can slow down innovation and increase operational overhead.
In contrast, NATS offers a lightweight, high-performance messaging system that streamlines these interactions and reduces architectural complexity. NATS removes the need for complex routing layers, external coordination services, and fragile networking dependencies.
Whether you’re deploying autonomous systems, real-time AI inferencing, or distributed microservices, NATS delivers fast, secure, and resilient communication—without the usual architectural bloat.
Let’s explore how NATS makes edge and AI-driven microservices leaner, more scalable, and easier to manage.
NATS for Microservices
Microservices rely on efficient, resilient, and scalable communication patterns. Traditional architectures often require message brokers, service discovery tools, and load balancers—but NATS eliminates these dependencies with a powerful yet simple publish-subscribe and request-reply model.
Key Features for Microservices
- Subject-Based Request-Reply: Unlike rigid RESTful APIs, NATS uses subject-based addressing instead of URLs. Clients can dynamically respond to subjects, enabling seamless microservices communication.
- Distributed Queuing with Geo-Affinity: Workload distribution happens automatically across available consumers, even across data centers.
Flexible Messaging Patterns:
- Request-Reply: Ideal for microservices that need immediate responses.
- Request Many: Gather multiple responses from different services.
- Work Queue Streaming: Efficient task distribution without bottlenecks.
Observability, Security, and Authorization Made Simple
- Subject Hierarchies with Wildcards: Instead of managing complex routing tables or service discovery tools, NATS lets you observe and control message flows with wildcard subjects (e.g., service.* to monitor all service-related traffic).
- Built-in Security: TLS, mTLS, and JWT-based authentication ensure secure communication without additional proxies or VPNs.
What You No Longer Need With NATS
- DNS & Service Discovery
- Load Balancers
- Reverse Proxies
- API Gateways
By reducing the need for these components, NATS dramatically reduces architectural complexity, improving performance, reliability, and cost-efficiency. This makes deploying, scaling, and managing NATS incredibly easy compared to traditional messaging systems.
NATS at the Edge
As computing moves closer to devices—whether self-driving cars, retail stores, or industrial automation—NATS shines as a messaging solution for the edge.
Lightweight & Versatile Deployment
- Single 15MB Binary: The entire NATS server fits into a small static Go binary.
- Zero External Dependencies: No need for databases or coordination services like ZooKeeper.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Runs seamlessly across 4 operating systems and 7 CPU architectures (Linux, macOS, Windows, and more).
Flexible Topologies for Any Environment
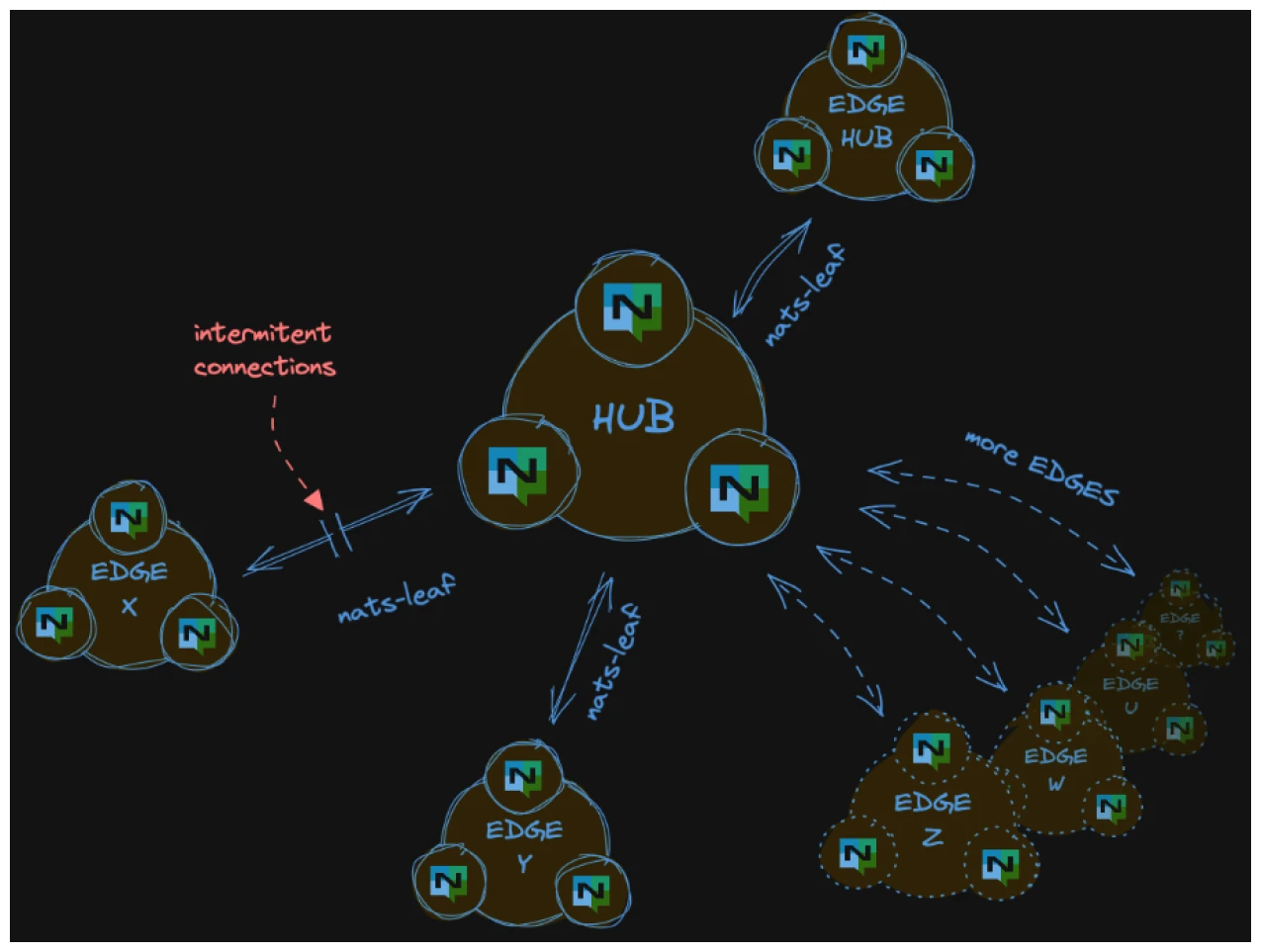
- Hub-and-Spoke (Leaf Nodes): Connect edge devices back to a central hub while still allowing local communication when disconnected.
- Mesh Networking: Peer-to-peer connectivity between edge devices, even across unreliable networks.
Reliable Data Handling in Intermittent Environments
- Guaranteed Store & Forward: NATS JetStream ensures that messages persist even when connectivity is lost, making it ideal for remote deployments.
- Security Across Boundaries: With mTLS and JWT-based access control, NATS ensures that edge devices communicate securely without requiring VPNs.
Example Use Cases:
In the context of autonomous vehicles, NATS can play a crucial role. For example, a fleet of autonomous vehicles might use NATS to stream critical telemetry data— GPS coordinates, sensor readings, environmental conditions, etc—to a central monitoring system in real time. Moreover, if connectivity to the central system is lost, each vehicle can rely on local decision-making powered by pre-loaded algorithms, ensuring safe and continuous operation despite intermittent network availability. All with no data lost.
In industrial IoT scenarios, NATS can similarly enhance operational efficiency. Imagine factory sensors that continuously monitor equipment temperature, vibration, or power fluctuations. By leveraging NATS, these sensors can instantly transmit real-time alerts to maintenance teams when anomalies are detected. And if a continuous connection to a central server isn’t available, the natural store and forward capabilities of NATS leaf nodes take over.
NATS in AI Applications
AI and machine learning workloads often require fast, reliable, and scalable data pipelines. NATS facilitates real-time data flow between edge devices and the cloud, making it a natural fit for AI-driven applications.
Data Flow - Within the Edge:
High-frequency sensor data is streamed to local inference engines.
Data Flow - Edge-to-Cloud:
Critical events (e.g., detected anomalies) are forwarded to cloud-based AI models.
AI-Driven Edge Superpowers
- Leaf Nodes for AI Model Updates: Easily distribute updated AI models to edge devices without complex orchestration.
- Seamless Cloud Integration: Move AI workloads between edge and cloud without introducing latency bottlenecks.
Example: A smart retail store can use NATS to process local video analytics, only sending valuable events (e.g., suspected fraud, operational errors) to the cloud for deeper analysis.
Conclusion
NATS is more than just a message broker—it’s a simplification engine for modern applications. Whether you’re building microservices, deploying at the edge, or optimizing AI pipelines, NATS removes unnecessary complexity, making your architecture more resilient, scalable, and efficient.
Need help deploying NATS for your edge and AI applications? Contact us to learn how Synadia can help you get to prod faster, safer, and with less stress.
